The shift from traditional monolithic ecommerce platforms to microservice-driven ecommerce platforms has proven to be a revolutionary transformation in ecommerce. Microservices provide a modular approach for retailers that allows applications to be connected as a collection of independent services. Instead of all-in-one monolithic platforms where components are tightly integrated, microservices-driven ecommerce platforms offer retailers the benefits of enhanced flexibility, scalability, and agility. This change in strategy has changed the standard for structuring and maintaining ecommerce platforms.
Microservice-driven ecommerce platforms break down the unified system application into multiple service modules and each module communicates seamlessly with others. These microservices components are crucial as they empower retailers to create customer-centric shopping experiences.
In this blog, we’ll list seven different microservice components and discuss how they collectively contribute to the success of modern ecommerce platforms.
What You’ll Discover
- Microservices Evolution: Explore how microservices reshape ecommerce, moving from traditional monolithic systems to a modular, flexible approach.
- Microservices Components Insight: Understand the concept of microservices with incorporated components, creating adaptable and scalable applications.
- The Core of Microservices Platforms: Uncover the basis of microservices-driven ecommerce platforms to learn how the components provide agility and responsiveness.
- Ecommerce Microservices Layers: Break down the four layers of ecommerce microservices architecture, from data storage to the user interface.
- Benefits of Replatforming: Discover the benefits, including team collaboration, scalability, fault isolation, independent deployability, tech flexibility, and data security precision.
- Essential Platform Components: Explore the microservices’ key components such as ecommerce/shopping cart, order management, payment processing, CRM, inventory management, marketing automation, and analytics/reporting.
Read More: Microservice-Based Solutions for Scalable Retail Agility
The fundamental idea of a microservices-driven ecommerce platform revolves around breaking down the traditional approach of monolithic systems into specialized components known as microservices.
In simpler terms, each microservice is like a small, dedicated application with a specific task. Unlike the tightly-knit structure of monolithic platforms, these microservices operate independently, making them easily replaceable and independent. They work together seamlessly to create the backbone of an ecommerce platform.
The brilliance of ecommerce microservices lies in their collaboration. They are like a team of specialists, each excelling in a specific area of the online business – from managing orders and processing payments to handling customer relationships and inventory. This streamlines the development process to enhance flexibility, scalability, and adaptability.
After replatforming to a microservices-driven ecommerce platform, retailers can create a solution that adapts to the changing demands of online shoppers. This change simplifies the complexities of building and maintaining ecommerce platforms to provide a scalable solution.
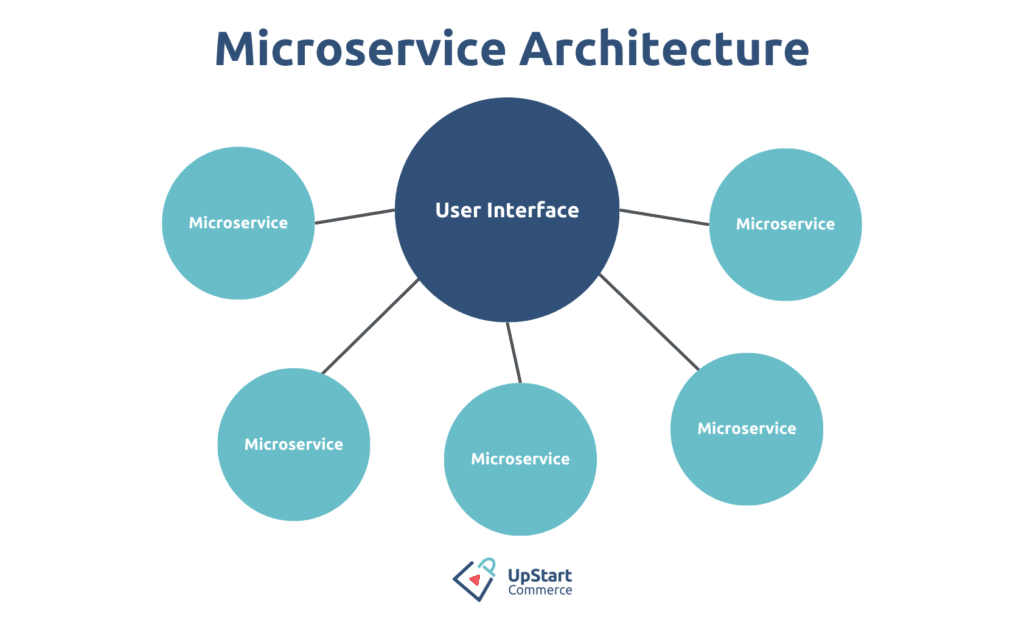
Ecommerce Microservices Architecture
In ecommerce, microservices act as the engine. The ecommerce microservices architecture is made of four main layers that work together. Each layer has a unique role, contributing to the ecommerce experience.
Data Storage Layer
The data storage layer acts as the digital warehouse. It contains databases that hold crucial information like inventory, product listings, and more. Each cluster, like inventory or product details, has a separate space in this warehouse. Microservices retrieve data from various databases present in this layer.
Microservices Layer
In an ecommerce platform, microservices do all the heavy lifting. These are like specialized teams, loosely coupled yet grouped by function. One team handles payments and another manages orders, teamwork at its finest!
Routing Layer
The routing layer serves as the traffic controller and ensures that when a user searches for something, their request goes to the right microservice. It’s like a guide to ensure everything flows smoothly, from handling load balancing to network details and security.
User Interface Layer
The user interface layer is what a user interacts with. It’s like the storefront window of a physical shop but in the digital world. This layer is the public face of the ecommerce world.
Microservice-driven ecommerce platforms have numerous benefits. Let’s explore some of them:
Unlocking Team Collaboration
Microservice-driven ecommerce platforms can simultaneously work across development teams. Unlike traditional approaches, microservices allow multiple teams to work on different aspects of the platform at the same time. This increases collaboration, accelerates development timelines, and allows for more efficient project execution.
Scaling Effortlessly to Meet Demand
Since individual components can scale independently, retailers can adapt to varying workloads and changing demands. This scalability ensures that localized areas of the platform can change based on real-time needs, optimizing resource utilization to enhance overall system performance.
Enhanced Troubleshooting with Fault Isolation
Microservices improve fault isolation. If an issue arises in one microservice, it won’t impact the entire ecommerce ecosystem. This troubleshooting improvement makes it easier to address problems without causing widespread disruptions and ensures a stable ecommerce platform.
Deploying Changes Independently
Independent deployability is a game-changer for microservice-driven ecommerce platforms. Unlike monolithic architectures where updates may require the entire system to be brought down, microservices allow for independent deployment of updates and new features. This reduces downtime, minimizes disruptions, and facilitates a more agile release cycle.
Flexibility in Tech Choices
Microservices offer businesses the flexibility to have more options in technology choices. Each microservice can be developed with different technologies, allowing retailers to use the best tools for the specific requirements of each service. This allows the platform to remain at the forefront of technological advancements.
Securing Data with Precision
Ensuring data security is a primary concern in ecommerce. With the ability to implement security measures tailored to each microservice, retailers can increase overall data protection. This granular approach enables security protocols to be precisely configured based on the sensitivity of the data.
Read More: Enhancing Microservices Security: The Role of API Gateway and Service Mesh
Now, let’s take a closer look into the essential components that make up a microservices-driven ecommerce platform:
The shopping cart is the heartbeat of the online shopping experience. It includes a set of tools and features that provide customers with a streamlined checkout process that creates a smooth customer journey.
Read More: Optimizing the Mobile Cart Experience with UpStart Commerce
Order Management
It is important to manage orders and shipments efficiently. Order management microservices provide features like an order-tracking system and seamless integration with shipping carriers. It ensures that retailers handle orders with precision, from the point of purchase to delivery.
Payment Processing
Payment processing encompasses the financial aspect of online transactions. It includes tools for accepting and processing payments and integrates with various payment gateways to ensure a secure payment process for customers.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Building and maintaining strong customer relationships is the core of any successful ecommerce business. The CRM provides tools for managing customer data and interactions. This includes a customer database, email marketing tools, and API endpoints for integration with customer service platforms.
Inventory Management
Keeping track of real-time inventory levels is important for efficient operations. Inventory management includes tools for managing inventory and integrates with inventory management systems to provide accurate updates on stock levels. It ensures that retailers can optimize stock to meet customer demand.
Marketing Automation
Promoting products is easier with marketing automation. These tools automate marketing efforts, such as email marketing, social media marketing, and targeted advertising. The flexibility of APIs allows businesses to integrate with their preferred systems and connect all data points for a comprehensive marketing strategy.
Read More: The Benefits of Ecommerce Promotions in 2024
Analytics and Reporting
Understanding your business data is crucial for growth. Analytics and reporting empower businesses to take a deeper look into various aspects, including website traffic, sales, and customer behavior. The system utilizes relevant data points to construct easy-to-read dashboards, providing valuable insights for informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
A microservices-driven ecommerce platform is like a complete package. It uses individual components to make an online shopping experience that’s adaptable, scalable, and focused on customers.